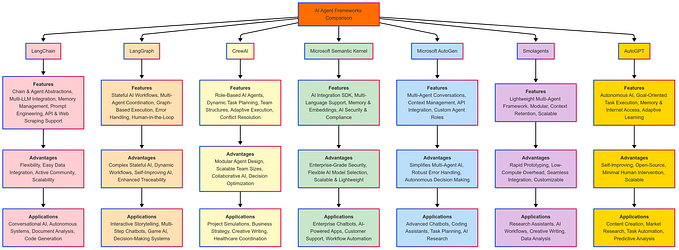
When to Use a Simple AI Agent vs. an Agentic AI System
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, businesses and developers face an important question: should they use a simple AI agent or an agentic AI system? While both have their place in modern applications, choosing the right type of AI depends on factors such as complexity, autonomy, adaptability, and decision-making requirements.
A simple AI agent is designed to perform specific tasks based on predefined rules and models, while an agentic AI system can set its own goals, adapt to changing conditions, and make complex decisions without continuous human oversight. Understanding the key differences and use cases for each can help organizations optimize efficiency, reduce risks, and maximize AI’s potential.
What is a Simple AI Agent?
A simple AI agent is a software system that interacts with its environment to execute tasks based on predefined rules or learned patterns. These agents operate within strict boundaries and typically follow a reactive approach, meaning they respond to inputs but do not independently set new objectives.
When to Use a Simple AI Agent
- Repetitive and Well-Defined Tasks Simple AI agents are ideal for tasks that have clear rules and structured inputs. Examples include chatbots for customer service, recommendation engines in e-commerce, and automated data processing in business applications.
- Low-Risk Environments Since simple AI agents operate within predefined parameters, they are best suited for environments where decision-making errors have minimal consequences. For example, an AI-powered email filter that sorts spam is effective but does not pose significant risks if it occasionally misclassifies an email.
- Fast and Efficient Execution When speed and efficiency are priorities, simple AI agents are preferred. They require fewer computational resources compared to more advanced AI systems and can deliver instant results without the need for extensive training or adaptation.
- Limited Need for Adaptability If the system does not require continuous learning or adaptation to changing conditions, a simple AI agent is sufficient. Virtual assistants that provide weather updates or automated billing systems fall into this category.
- Regulatory and Compliance Constraints In industries with strict regulations, such as finance and healthcare, simple AI agents are often favored because they offer greater predictability and traceability in decision-making, reducing the risk of unintended consequences.
What is an Agentic AI System?
An agentic AI system goes beyond basic automation by making independent decisions, adapting to new information, and setting its own objectives within broader goals. These systems leverage machine learning, reinforcement learning, and real-time data analysis to optimize processes without requiring constant human intervention.
When to Use an Agentic AI System
- Complex Decision-Making with Uncertain Inputs Agentic AI is best suited for scenarios where the system must evaluate multiple variables and make decisions based on evolving data. Autonomous vehicles, for instance, must interpret real-time road conditions, predict other drivers’ behaviors, and adjust their actions accordingly.
- Dynamic and Rapidly Changing Environments In industries such as cybersecurity and financial trading, where conditions change rapidly, agentic AI can react in real time to threats, market fluctuations, or unexpected events, making it far more effective than static rule-based systems.
- Long-Term Optimization and Strategy When businesses need AI to not only complete tasks but also optimize long-term outcomes, agentic AI is the right choice. For example, an AI-powered supply chain system can analyze global logistics trends, anticipate disruptions, and proactively adjust inventory management.
- Reducing Human Oversight in Large-Scale Operations Some applications require AI to operate with minimal human intervention due to the scale and complexity of the tasks. Smart grids that autonomously balance energy distribution or AI-driven drug discovery platforms that analyze millions of chemical compounds fall into this category.
- Continuous Learning and Self-Improvement Unlike simple AI agents, agentic AI can improve over time by learning from past interactions. Personalized healthcare treatment plans, AI-driven business strategy recommendations, and fraud detection systems benefit from this capability.
Choosing the Right AI for Your Needs
When deciding between a simple AI agent and an agentic AI system, organizations should consider the following factors:
- Complexity of the Task: If the task is straightforward and rule-based, a simple AI agent is the best choice. If it involves multi-step reasoning and adaptation, agentic AI is more suitable.
- Level of Risk: Higher-risk applications, such as medical diagnostics or autonomous decision-making, may require agentic AI with strong oversight mechanisms.
- Need for Adaptability: If the AI must continuously learn and adjust its approach, an agentic AI system is necessary.
- Computational Resources: Simple AI agents require fewer resources, making them more cost-effective for basic automation. Agentic AI systems, however, need significant computational power and training data.
Both simple AI agents and agentic AI systems play important roles in the AI landscape. While simple AI agents are excellent for efficiency, automation, and rule-based tasks, agentic AI systems are better suited for complex, evolving scenarios that require adaptability and strategic decision-making.
By carefully assessing business needs, risk factors, and computational requirements, organizations can determine whether to deploy a simple AI agent for well-defined tasks or invest in agentic AI for more autonomous, long-term optimization. As AI continues to evolve, making the right choice will be key to unlocking the full potential of artificial intelligence in business and beyond.